Advanced decision support
CIPCast Web Description
One of the major R&D activities carried out in CIPRNet has been focussed on the design and the realisation of a prototyping of a Decision Support System (DSS) for the effect of uncertainty on objectives
[Click for more information]risk forecast of See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI elements. The Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS, addressing different players involved in the emergency management operations (e.g. See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI operators, Civil Protection, Public Administration), solves the problem of estimating the threats to which each element of See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI is subjected due to extreme events (either of geophysical or meteo-climatological origin), the damage that they could inflict, the subsequent reduction or loss of functionality of all See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI involved (also through cascading effects) and the related consequences on society (citizens, goods, land etc.)
The Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS conceptual workflow is divided in different phases:
Sensing the environment: The Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS gathers external field data as for example seismic monitoring networks, meteorological satellites network, now-casting radar monitoring network, data from weather stations, river hydrometers and satellite Images. The system can also read other data source from any type of sensors located in the environment.
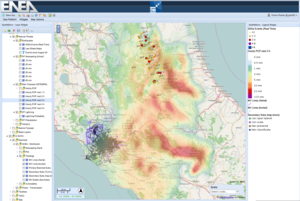
[Click for more information]CI in the area. Rainfall nowcasting data visible in the north part of the earthquake areas (© ENEA)
An event describes what happens to a component in the CI model if a condition is fulfilled, e.g. the tripping of a transmission line at a certain time.
[Click for more information]Event forecast and/or/event detection: External field data are used to forecast various natural hazards within a specified Forecast Interval (e.g. 48 hours). For example, meteorological data can be used to forecast rain precipitation in a specific area. Such data can input appropriate hydrological models of specific areas to forecast a flooding source of potential harm
[Click for more information]hazard. In case of an earthquake, the Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS has an earthquake propagation simulator, enabling the estimate of the seismic intensity (macro-seismic intensity, peak ground accelerations) in the hit area.
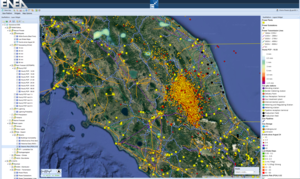
[Click for more information]CI elements due by a real or simulated earthquake (© ENEA)
Predicting damage A scenario consists of a CI model, the initial states of all components and the scenario behaviour that describes the events that happen within the scenario.
[Click for more information]scenario: Possible damages inflicted to different See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI elements are highlighted and prompted to the attention of See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI operators and/or other Public Authorities committed in crisis management under the form of a Report. The Damage A scenario consists of a CI model, the initial states of all components and the scenario behaviour that describes the events that happen within the scenario.
[Click for more information]Scenario Report describes the affected See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI components, the possible causes of the damages, the time in which damage is expected to occur and the damage extent. See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI elements intrinsic properties of something resulting in susceptibility to a risk source that can lead to an event with a consequence
[Click for more information]vulnerability to different threats has been estimated by using historical data, technical data and assessment based on empirical functions (such as building seismic vulnerability).
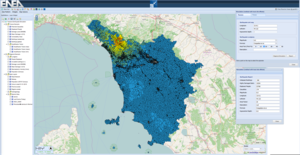
[Click for more information]Consequence analysis of a crisis A scenario consists of a CI model, the initial states of all components and the scenario behaviour that describes the events that happen within the scenario.
[Click for more information]scenario produced by a bi-centennial Tiber flooding in the north area of Roma. Different colours represent different values of the Kmin metrics estimated in the different areas hit by electrical outages
Estimating Impacts: Through a purposely realised simulator of cascading failures, the Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS estimates the impacts caused by the expected damages, on the functioning of the hit See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI and of that of the other See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI perturbed through cascading phenomena. The Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS database also contains the Dependency is the relationship between two (critical infrastructure) products or services in which one product or service is required for the generation of the other product or service.
[Click for more information]dependency map connecting each See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI element with the other See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI elements to which they provide services and/or from which they receive services.
outcome of an event affecting objectives
[Click for more information]Consequence Analysis: The impact A scenario consists of a CI model, the initial states of all components and the scenario behaviour that describes the events that happen within the scenario.
[Click for more information]scenario is estimated in terms of unavailability of a number of See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI elements, due to damages, failures for intra-network perturbation diffusion and inter-network cascading effects. The Impact Report is also promptly sent to See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI operators and Authorities.Other that the mere list of the expected unavailable services, CIPCast solves the problem of estimating the best strategy for recovering the network(s) functionality: its internal tool GeoRecSIM emulates the actions performed by the See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI operators (tele-measure that is modifying risk
[Click for more information]control operations, dispatching of technical teams to perform elements restoration etc.) to locate the optimal strategy for service(s) restoration(s) (a strategy is the sequence of interventions needed to the available technical teams to restore all service losses and to allow to restore the situation before the event). Optimisation is carried out by evaluating the resulting crisis intensity as a function of all possible recovery strategies by using several metric:
- Service Continuity Index (Kmin)
- Economic damages to the industrial sectors (ED)
- Reduction of wealth to citizens (ΔW)
Kmin indicates the total sum of the number of citizens involved in the outage fo some service times the period of the loss of that(those) service(s).ED estimates the total revenue losses experienced by the industrial activities when deprived by specific services ΔW estimates the reduction of well being ("wealth") of people when deprived by primary services as those supplied by See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI.
Decision support: The Decision Support System
[Click for more information]DSS consolidates the "crisis assessment" by delivering a Final Report of the predicted crisis to all the players involved in the operations, from See critical infrastructure
[Click for more information]CI operators to Civil Protection, to Public Administration in a way to allow all them to have a common set on information on which they could properly elaborate coherent mitigation and healing strategies and, whenever the case, Emergency plans.